这个世界上肯定有另一个我,做着我不敢做的事,过着我想过的生活。挑战自己不擅长的事,敢于说走就做的旅行,每天做很多新鲜的事。极致的幸福,存在于孤独的深海。在这样日复一日的生活里,我逐渐和自己达成和解。
1. ORACLE的启动和关闭
1、在单机环境下
要想启动或关闭ORACLE系统必须首先切换到ORACLE用户,如下
su - oracle
a、启动ORACLE系统
oracle>svrmgrl
SVRMGR>connect internal
SVRMGR>startup
SVRMGR>quit
b、关闭ORACLE系统
oracle>svrmgrl
SVRMGR>connect internal
SVRMGR>shutdown
SVRMGR>quit
启动oracle9i数据库命令:
$ sqlplus /nolog
SQL*Plus: Release 9.2.0.1.0 - Production on Fri Oct 31 13:53:53 2003
Copyright (c) 1982, 2002, Oracle Corporation. All rights reserved.
SQL> connect / as sysdba
Connected to an idle instance.
SQL> startup^C
SQL> startup
ORACLE instance started.
2、在双机环境下
要想启动或关闭ORACLE系统必须首先切换到root用户,如下 su - root a、启动ORACLE系统 hareg -y oracle b、关闭ORACLE系统 hareg -n oracle Oracle数据库有哪几种启动方式
2. 导入数据
C:\Users\tony>sqlldr
SQL*Loader: Release 11.2.0.1.0 - Production on 星期六 9月 3 09:12:45 2011
Copyright (c) 1982, 2009, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
用法: SQLLDR keyword=value [,keyword=value,...]
有效的关键字:
userid -- ORACLE 用户名/口令
control -- 控制文件名
log -- 日志文件名
bad -- 错误文件名
data -- 数据文件名
discard -- 废弃文件名
discardmax -- 允许废弃的文件的数目 (全部默认)
skip -- 要跳过的逻辑记录的数目 (默认 0)
load -- 要加载的逻辑记录的数目 (全部默认)
errors -- 允许的错误的数目 (默认 50)
rows -- 常规路径绑定数组中或直接路径保存数据间的行数
(默认: 常规路径 64, 所有直接路径)
bindsize -- 常规路径绑定数组的大小 (以字节计) (默认 256000)
silent -- 运行过程中隐藏消息 (标题,反馈,错误,废弃,分区)
direct -- 使用直接路径 (默认 FALSE)
parfile -- 参数文件: 包含参数说明的文件的名称
parallel -- 执行并行加载 (默认 FALSE)
使用的默认的, 没有加入 direct=true .
执行的脚本类似:
$ sqlldr [email=user1/passwd1@db1]user1/passwd1@db1[/email] control=xxx.ctl
3. 函数与存储过程
1. 函数demo:
create or replace procedure sy_merge_label(
par1 varchar2 in,
par2 varchar2 out
) as
CURSOR C_LABEL IS
select rownum,ENT_MD5,ENT_LABEL from crt_ent_label group by ENT_MD5;
C_ROW C_LABEL%ROWTYPE;
rown int;
md5 varchar2;
md5_old int:=0;
label varchar2;
TYPE arry_num IS VARRAY(100) OF NUMBER;
rownums arry_num;
begin
FOR C_ROW IN C_LABEL LOOP
--处理逻辑
rown:=C_ROW.rownum;
md5:= C_ROW.ENT_MD5;
label:=C_ROW.ENT_LABEL;
if label in ('医学考试') then
--if md5_old != md5 then
--else
--DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(md5||label)
end if
END LOOP
EXCEPTION
WHEN no_data_found THEN
raise_application_error(-20000, '该员工不存在');
end sy_merge_label
2. 解释: PL/SQL中的过程和函数(通常称为子程序)是PL/SQL块的一种特殊的类型,这种类型的子程序可以以编译的形式存放在数据库中,并为后续的程序块调用。
相同点: 完成特定功能的程序
不同点:是否用return语句返回值。 举个例子:
create or replace procedure PrintStudents(p_staffName in xgj_test.username%type) as
cursor c_testData is
select t.sal, t.comm from xgj_test t where t.username = p_staffName;
begin
for v_info in c_testData loop
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(v_info.sal || ' ' || v_info.comm);
end loop;
end PrintStudents;
一旦创建了改程序并将其存储在数据库中,就可以使用如下的方式调用该过程
begin
PrintStudents('Computer Science');
PrintStudents('Match');
end;
/
或者
exec PrintStudents('Computer Science');
exec PrintStudents('Match');
在命令窗口中:

在pl/sql工具的sql窗口中:
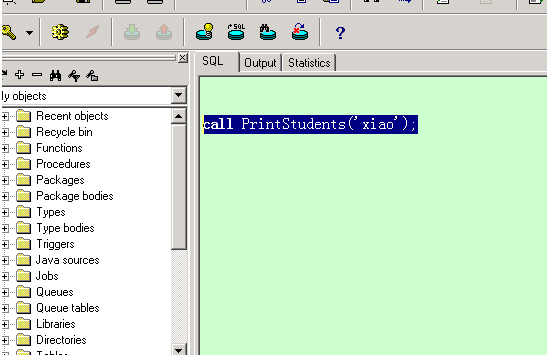
** 存储过程的创建和调用
基本语法 **
create [ or replace] procedure procedure_name
[( argument [ {IN | OUT | IN OUT }] type,
......
argument [ {IN | OUT | IN OUT }] type ) ] { IS | AS}
procedure_body
无参的存储过程
/**
无参数的存过
打印hello world
调用存储过程:
1. exec sayhelloworld();
2 begin
sayhelloworld();
end;
/
*/
create or replace procedure sayhelloworld
as
--说明部分
begin
dbms_output.put_line('hello world');
end sayhelloworld;
调用过程:
SQL> set serveroutput on ;
SQL> exec sayhelloworld();
hello world
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed
SQL> begin
2 sayhelloworld();
3 sayhelloworld();
4 end;
5 /
hello world
hello world
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed
带参数的存储过程
/**
创建一个带参数的存储过程
给指定的员工增加工资,并打印增长前后的工资
*/
create or replace procedure addSalary(staffName in xgj_test.username%type )
as
--定义一个变量保存调整之前的薪水
oldSalary xgj_test.sal%type;
begin
--查询员工涨之前的薪水
select t.sal into oldSalary from xgj_test t where t.username=staffName;
--调整薪水
update xgj_test t set t.sal = sal+1000 where t.username=staffName ;
--输出
dbms_output.put_line('调整之前的薪水:'|| oldSalary || ' ,调整之后的薪水:' || (oldSalary + 1000));
end addSalary;
可以看到,update语句之后并没有commit的操作。
一般来讲为了保证事务的一致性,由调用者来提交比较合适,当然了是需要区分具体的业务需求的~
begin
addSalary('xiao');
addSalary('gong');
commit ;
end ;
/
2.存储函数
基本语法
create [ or replace] function function_name
[( argument [ {IN | OUT | IN OUT }] type,
......
argument [ {IN | OUT | IN OUT }] type ) ]
RETURN { IS | AS}
function_body
其中 return子句是必须存在的,一个函数如果没有执行return就结束将发生错误,这一点和存过有说不同
/**
查询员工的年薪 (月工资*12 + 奖金)
*/
create or replace function querySalaryInCome(staffName in varchar2)
return number as
--定义变量保存员工的工资和奖金
pSalary xgj_test.sal%type;
pComm xgj_test.comm%type;
begin
--查询员工的工资和奖金
select t.sal, t.comm
into pSalary, pComm
from xgj_test t
where t.username = staffName;
--直接返回年薪
return pSalary * 12 + pComm;
end querySalaryInCome;
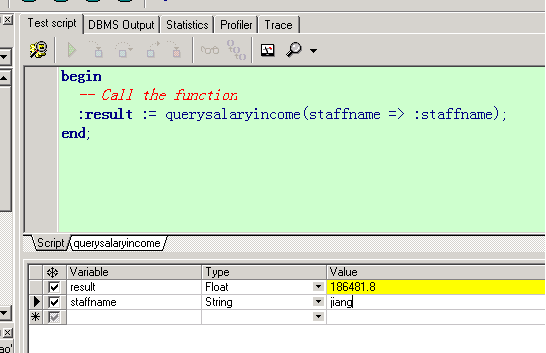
存在一个问题,当奖金为空的时候,算出来的年收入竟然是空的。
因为 如果一个表达式中有空值,那么这个表达式的结果即为空值。
所以我们需要对空值进行处理, 使用nvl函数即可。
最后修改后的function为
create or replace function querySalaryInCome(staffName in varchar2)
return number as
--定义变量保存员工的工资和奖金
pSalary xgj_test.sal%type;
pComm xgj_test.comm%type;
begin
--查询员工的工资和奖金
select t.sal, t.comm
into pSalary, pComm
from xgj_test t
where t.username = staffName;
--直接返回年薪
return pSalary * 12 + nvl(pComm,0);
end querySalaryInCome;
out参数 一般来讲,存储过程和存储函数的区别在于存储函数可以有一个返回值,而存储过程没有返回值。 1.存储过程和存储函数都可以有out参数 2.存储过程和存储函数都可以有多个out参数 3.存储过程可以通过out参数实现返回值
那我们如何选择存储过程和存储函数呢?
原则:
如果只有一个返回值,用存储函数,否则(即没有返回值或者有多个返回值)使用存储过程。
/**
根据员工姓名,查询员工的全部信息
*/
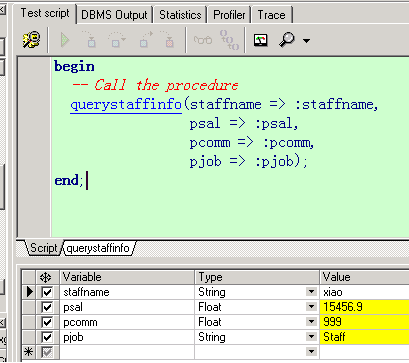
create or replace procedure QueryStaffInfo(staffName in xgj_test.username%type,
pSal out number,
pComm out xgj_test.comm%type,
pJob out xgj_test.job%type)
is
begin
--查询该员工的薪资,奖金和职位
select t.sal,t.comm,t.job into pSal,pComm,pJob from xgj_test t where t.username=staffName;
end QueryStaffInfo;
先抛出两个思考问题: 1.查询员工的所有信息–> out参数太多怎么办? 2.查询某个部门中所有员工的信息–> out中返回集合?
后面会讲到如何解决? 总不能一个个的写out吧~
3. 在应用中访问存储过程和存储函数
详情请访问原文链接
总结
整个文章的基本组织结构依照典型的工科思维方式进行串接,即从理论到实践。